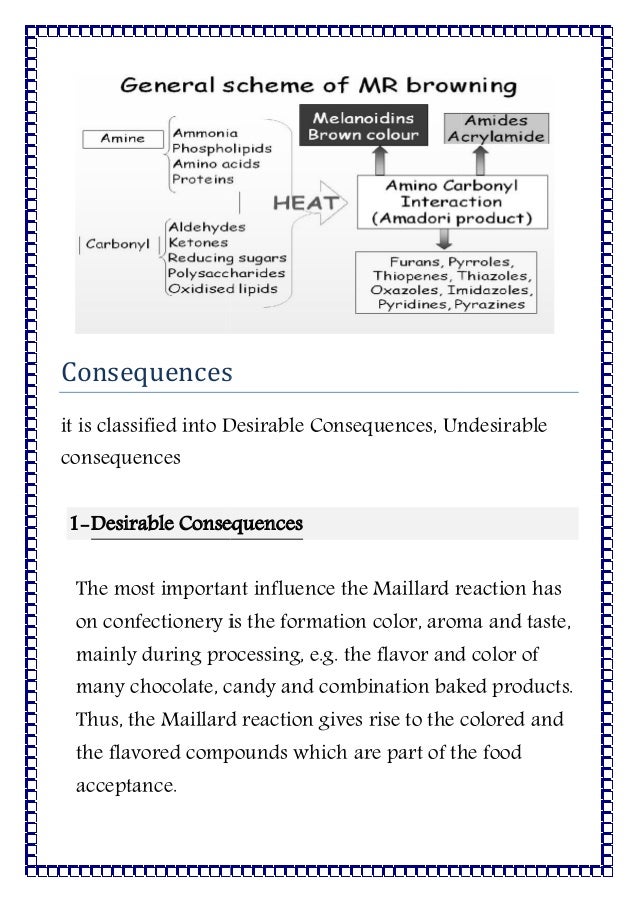
Maillard Reaction Definition
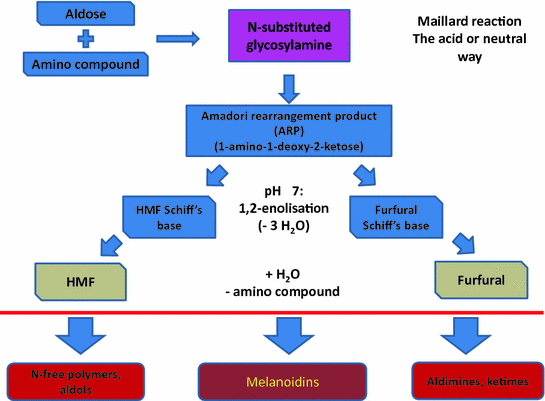
The reaction is named after the french chemist louis camille maillard 18781936 who stumbled on it while trying to replicate biological protein synthesis around 1910. A non enzymatic heat activated chemical reaction between sugars especially ribose and amino acids which occurs in foods as they form glycosylamines and amadori compounds.

Maillard Reaction
It results from a chemical reaction between an amino acid and a reducing sugar usually requiring heat.
Maillard reaction definition. The maillard reaction m aɪ ˈ j ɑːr my yar. The maillard reaction is a cooking phenomenon that occurs when amino acids and reducing sugars combine causing them to turn brown and yield a distinctive flavor. Like caramelization it is a form of non enzymatic browning.
The maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between an amino acid and a reducing sugar usually requiring the addition of heat. Like caramelization it is a form of non enzymatic browning. Maillard reaction definition is a nonenzymatic reaction between sugars and proteins that occurs upon heating and that produces browning of some foods such as meat and bread.
The maillard reaction produces water and so can be a cause of raised a w but the effect of a w on the maillard reaction is of much greater interest. It can occur in meats and proteins along with other foods including pan fried dumplings cookies bread toasted marshmallows and more. Seared steaks fried dumplings cookies and other kinds of biscuits breads toasted marshmallows and many other foods undergo this reaction.
Vitally important in the preparation or presentation of many types of food it is named after chemist louis camille maillard who first described it in 1912 while attempting to reproduce biological protein synthesis. Since loss of water is part of the maillard reaction the mass action effect of water at high a w will tend to hinder the reaction as will the dilution of the reagents. The maillard reaction is responsible for browning of baked or cooked foods eg bread crusts and barbecued steak which are mutagenic by the ames assay.
Maillard reaction is a type of non enzymic browning that adds color and flavor to many types of processed food including beer. Is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. The maillard reaction is a form of nonenzymatic browning.
Analytical Methods For The Determination Of Maillard Reaction

Maillard Reaction And Formation Of Heterocyclic Flavor Compounds
Contemporary Chemistry Chemistry Journals Sciaeon
The Importance Of Maillard Reaction In Processed Foods Springerlink

Maillard Reaction

Maillard Reaction

Option F4 F5

Maillard Reaction Meaning Youtube
Maillard Reaction Steak