Maillard Reaction
The maillard reaction m aɪ ˈ j ɑːr my yar. Browning or the maillard reaction creates flavor and changes the color of food.
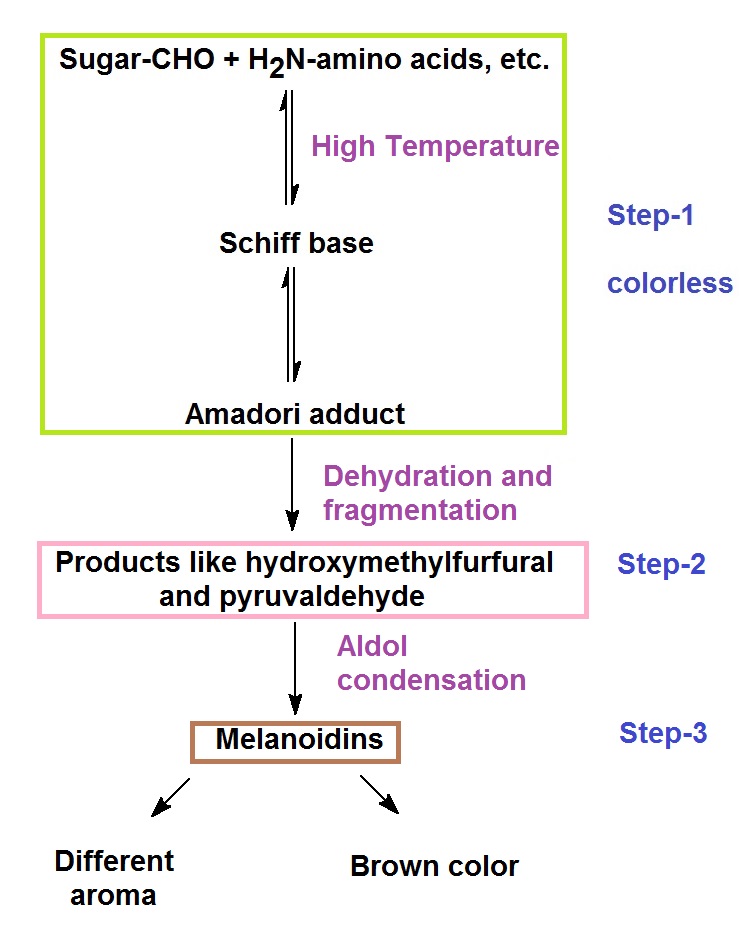
The Maillard Reaction And Amadori Rearrangement
Until the maillard reaction occurs meat will have less flavor.
Maillard reaction. Maillard reactions is the term used for a group of chemical reactions initiated by a condensation of an amino group with a reducing sugar as in the reaction of equation 162 and then followed by a cascade of reactions in foods leading to formation of different intermediates including aroma components and high molecular weight brown polymers nursten 2005. Maillard reaction definition is a nonenzymatic reaction between sugars and proteins that occurs upon heating and that produces browning of some foods such as meat and bread. The maillard reaction is evolutions way of combining these two signals into one super signal specific to the roasty or browned flavors of cooked food.
It makes food taste better. The important thing about the maillard reaction isnt the color its the flavors and aromas according to modernist cuisine by nathan myhrvold chris young and maxime bilet. Seared steaks fried dumplings cookies and other kinds of biscuits breads toasted marshmallows and many other foods undergo this reaction.
It is named after french chemist louis camille maillard who first described it. Is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Maillard reactions generally only begin to occur above 285f 140c.
Learn the science behind this essential chemical reaction and how it applies to cooking. Shown above are two identical dishes cooked left below 140c and right at much higher temperatures. The maillard reaction is the reaction between a nitrogen containing molecule particularly the amino acids lysine and proline in the case of meats and grains respectively and a reducing sugar.
Yes even beer undergoes the maillard reactionwhen the grains are roasted prior to brewing. This is why baking bread doesnt smell like roasting meat or frying fish even though all these foods depend on maillard reactions for flavor. The maillard reaction is an important culinary process responsible for new flavor aroma and color development.
The maillard reaction occurs in cooking of almost all kinds of foods although the simple sugars and amino acids present produce distinctly different aromas.

Food Browning Due Maillard Chemical Reaction Occurs Between Amino Aci

Proposed Maillard Reaction Products For Baclofen And Download

Maillard Reaction Baking Processes Bakerpedia

Maillard Reaction Mechanism Hard Core Chemistry Food Crumbles

Maillard Reaction Products Please Solve All Ques Chegg Com

1 A Proposed Mechanism Which Follows The Maillard Reaction For

Maillard Reaction In Milk Effect Of Heat Treatment Intechopen

The Maillard Reaction Picture It

Chemistry Net Food Chemistry The Browning Reaction Or Reactions